A group of researchers led by Cornell is unlocking the full potential of aluminum nitride – an important material for the advancement of electronics and photonics – thanks to the development of a surface cleaning technique that enables high-quality production.
The research was published Sept. 9 in the journal Science Advances. Graduate student Zexuan Zhang and research associate Yongjin Cho are the lead authors. The senior authors are Debdeep Jena and Huili Grace Xing, both professors of materials science and engineering and of electrical and computer engineering.
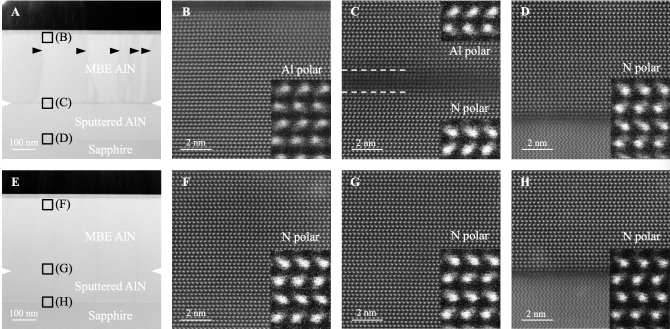
Cross-sectional microscopy images of molecular beam epitaxy-grown aluminum nitride on aluminum nitride templates. The black squares in (A) and (E) mark the regions where the corresponding magnified images (B to D and F to H) are taken. The white notches in (A) and (E) indicate the growth interfaces. The image contrasts in the molecular beam epitaxy layer and at the growth interface in sample A (A) are absent in sample B (E).
Aluminum nitride has gained significant research interest in the field of semiconductor materials as it provides an unmatched combination of high electrical resistivity and thermal conductivity, according to Zhang. The ceramic material is used as an electrically-insulating, but thermally-conducting, barrier in electronic devices, and due to its ability to operate at deep UV frequencies, it has great potential for use in light-emitting diodes and lasers.
The material’s polarity is a critical characteristic that can enhance its functionality, and exciting new performance advantages can be achieved in the nitrogen-polar form. However, materials scientists have yet to successfully produce a nitrogen-polar aluminum-nitride crystal on large-area native substrates using molecular beam epitaxy – a popular growth technique for high-quality heterostructures.
“Growing aluminum nitride on native substrates using molecular beam epitaxy has been hampered by difficulties with the removal of native oxides and other chemical impurities on aluminum-nitride wafers,” Cho said, “which lead to polarity inversion and defect formation at the growth interface.”
As a solution, the research team developed an aluminum-assisted surface cleaning technique that removes impurities from the substrates and enables the material to maintain its nitrogen polarity. Using this method, the team was able to demonstrate epitaxial growth of nitrogen-polar aluminum nitride with smooth surface morphology and high structural and optical quality.
“Thermally stable aluminum oxide present on aluminum nitride wafer surface reacts with aluminum and converts to a volatile form, eventually leading to oxide-free wafer surface for epitaxial growth,” Cho said, who added that the successful demonstration provides a proof-of-concept for nitrogen-polar electronic devices, which are believed to outperform their metal-polar counterparts that have been widely used for millimeter-wave applications.
Xing added, “The efficiency to generate deep ultra-violet photons is critically dependent on the defect control in aluminum nitride and its alloys. That is why we are excited about the progress made to grow higher quality materials on the aluminum-nitride platform.”
Co-authors of the research include graduate student Jashan Singhal, senior research associate Vladimir Protasenko, and researchers from Osaka University and Mie University. The research was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Air Force Office of Scientific Research, Cornell Center for Materials Research, the Kavli Institute at Cornell, and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.