Two new innovative methods describe how to measure the electrical resistivity of liquid iron—such as that found in planetary cores—at extremely high pressures and temperatures. Prior to this, there were no experimental measurements of the electrical resistivity of liquid iron beyond 51 GPa and 2,900 K. These findings will help derive better theoretical models for the puzzling properties of liquid iron.
Iron is the most abundant element by mass on Earth. Despite being so common and well-studied, iron still manages to puzzle scientists by exhibiting electric and magnetic behaviors that are not fully comprehensible. In particular, the physical properties of liquid iron—which makes up most of the Earth’s core—have been the subject of much debate among physicists and geoscientists.
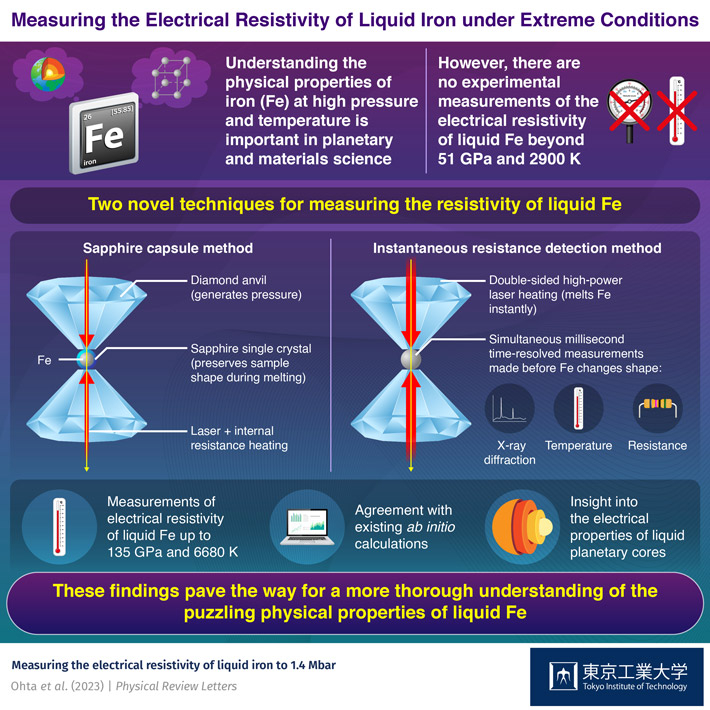
The problem is that certain predictions about liquid iron’s properties are difficult to experimentally verify due to the extreme conditions required to ascertain them. For example, liquid iron’s resistivity, which is the inverse of electrical conductivity, has only been measured up to 51 GPa pressure and 2,900 K temperature. This is because it is challenging to keep the iron sample’s shape and chemical composition intact within current high-pressure apparatus.
Against this backdrop, a research team including Associate Professor Kenji Ohta from Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan has recently achieved a breakthrough by measuring the electrical properties of liquid iron under extreme experimental conditions. As explained in their paper, which was published in Physical Review Letters, this was possible thanks to two new techniques that they developed.
Both techniques involved the use of a diamond anvil cell (DAC) that exerts incredibly high pressure on a sample by compressing it between the flat faces of two opposing diamonds. In the first technique, the researchers used a sapphire capsule to contain the iron sample in the DAC while heating it using a laser and electric current. “The idea was to keep the geometry of the iron sample unchanged during melting and to minimize temperature differences inside the sample,” explains Dr. Ohta.
The second technique involved a radically different approach. Instead of preserving the sample’s shape during the melting process by encapsulating it, the researchers used powerful lasers to ‘instantly’ melt the iron. The goal was to quickly and simultaneously measure millisecond-resolved resistance, x-ray diffraction, and temperature of the molten sample before it had enough time to change its geometry. This innovative strategy enabled the team to measure the resistivity of liquid iron at pressures and temperatures up to 135 GPa and 6,680 K, respectively.
Satisfied with the results, Dr. Ohta remarks: “Our measurements provide the experimentally constrained resistivity of liquid iron at pressures more than two times higher than those in previous experiments.”
Notably, the measurements revealed that the resistivity of liquid iron does not vary much with temperature. Moreover, it follows existing theoretical estimates at higher pressures quite well, including the anomalous decrease around 50 GPa, likely indicative of a gradual magnetic transition. This is important because there are some discrepancies between theoretical predictions and experimental data on the resistivity of liquid iron, especially at pressures below 50 GPa. Thus, the results of this study will help clarify the origin of these discrepancies and help physicists develop more accurate models and theories about the behavior of iron. In turn, this could lead to a more comprehensive understanding of terrestrial cores, as well as related phenomena such as planetary magnetic fields.
Reference
Authors : | Kenji Ohta1,*, Sho Suehiro1, Saori I. Kawaguchi2, Yoshiyuki Okuda1,3, Tatsuya Wakamatsu1, Kei Hirose3,4, Yasuo Ohishi2, Manabu Kodama5, Shuichiro Hirai5, and Shintaro Azuma1 |
Title : | Measuring the Electrical Resistivity of Liquid Iron to 1.4 Mbar |
Journal : | Physical Review Letters |
DOI : | |
Affiliations : | 1Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Tokyo Institute of Technology 2Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute, SPring-8 3Department of Earth and Planetary Science, The University of Tokyo 4Earth-Life Science Institute, Tokyo Institute of Technology 5Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology |








